What Are PCIe Slots And Their Uses? [Simplified Guide]
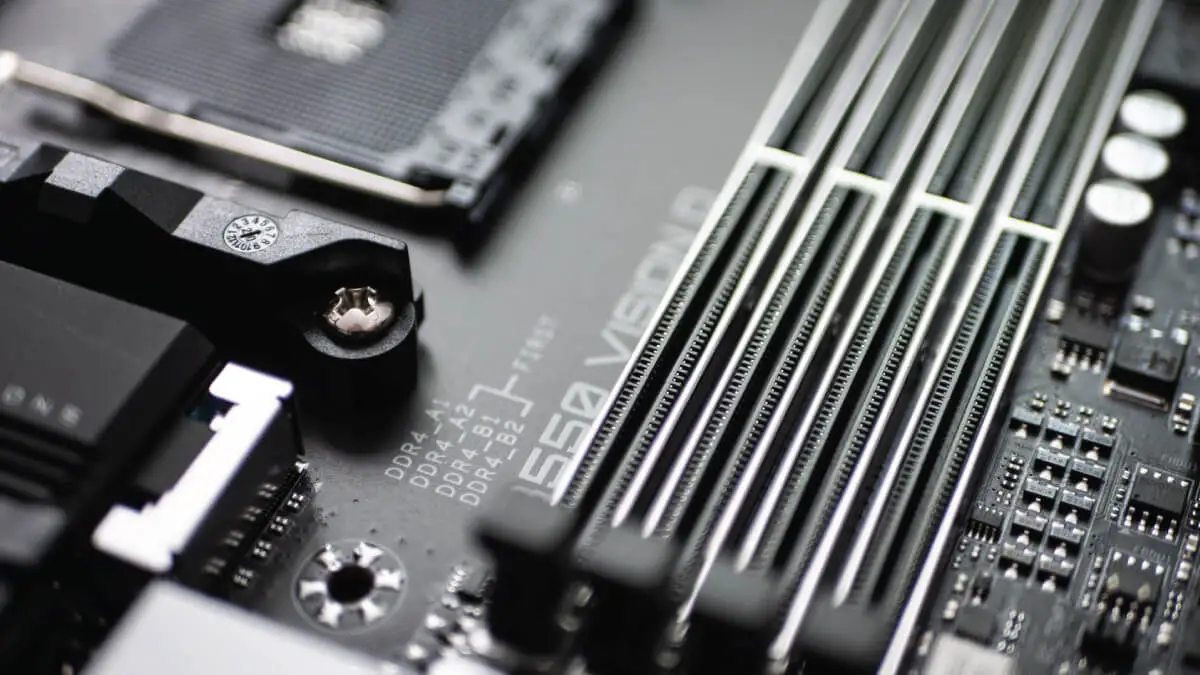

- PCIe slots are expansion slots on your motherboard.
- They’re used to connect more hardware parts to your motherboard to expand its functionality.
- PCIe slots come in different sizes like PCIe x1, PCIe x4, PCIe x8, PCIe x16, and PCIe x32.
- Major uses for PCIe slots include connecting GPUs, sound cards, SSD drives, Wifi cards, and so on.
So, here’s what you’re going through: you’ve either heard the name of PCIe slots or just saw them on your motherboard. Now, you’re wondering “what are PCIe slots and what they’re used for?”
PCIe refers to a peripheral component interconnect express. These are high-definition slots on your motherboard used to connect high-speed parts to your motherboard to expand its functionality. It could be a GPU you can add, a Wifi card, an SSD, and so on.
Here’s what this guide is going to get you through:
- What are the different types of PCIe expansion slots?
- What are the uses of PCIe slots?
- What are the small PCIe slots for, and so on?
With that out of the way, let’s roll in.
What Are PCIe Slots?


PCIe slots are expansion slots on your motherboard designed to connect additional hardware parts to your motherboard. PCIe slots offer high-speed connections and come in different configurations.
To best understand PCIe slots, here’s an example…
You use Chrome or another browser on your computer every day, don’t you? If you do, you might have installed some browser plugins like IDM, a VPN, an ad-blocker, or anything like that.
If you can relate to this example, suppose that the Chrome browser is your motherboard. Since Chrome offers the option to install extensions to improve its functionality, your motherboard also gives you that option through PCIe slots. The hardware parts you install are the extensions you install on Chrome.
Got the picture, right?
By the way, SATA ports are something else you may also be wondering about. Read our guide on what does a SATA port look like to find out more.
Now, what are the different types of PCIe expansion slots, and how to identify PCIe slots? Let’s find out.
What Are PCIe Slot Sizes or Configurations?
There’s a wide range of PCIe slot sizes. But there are 4 common types — and you’ll only encounter these in most cases:
- PCIe x1
- PCIe x4
- PCIe x8
- PCIe x16
These multiples refer to lanes. Generally, more lanes result in a better performance as they ensure a faster connection between the expansion hardware parts and the motherboard.


That’s exactly why high-performance devices like graphics cards go into PCIe x16.
Below is a detailed comparison of different PCIe versions.
| Version | x1(GB/s) | x2(GB/s) | x4(GB/s) | x8(GB/s) | x16(GB/s) |
| 1.0 | 0.250 GB/s | 0.500 GB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.000 GB/s | 4.000 GB/s |
| 2.0 | 0.500 GB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.000 GB/s | 4.000 GB/s | 8.000 GB/s |
| 3.0 | 0.985 GB/s | 1.969 GB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s |
| 4.0 | 1.969 GB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s |
| 5.0 | 3.938 GB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s | 63.015 GB/s |
| 6.0 | 7.877 GB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.508 GB/s | 63.015 GB/s | 126.031 GB/s |
Uses of Different PCIe Slot Sizes
Here we’ll look into the uses of different PCIe slot sizes:
What are PCIe x1 Slots Used for?
PCIe x1 slots only offer a single PCIe lane. It suits the small hardware pieces well — like Wifi and sound cards. You cannot install high-end devices like graphics cards on these slots due to low bandwidth.
What are PCIe x4 Slots Used for?
PCIe x 4 slots come with 4 PCIe lanes and have 4 times the bandwidth of PCIe x1 slots. You can use it for devices like 4k capture cards that take more bandwidth. Similarly, it can also make a fit with the NVMe M.2 SSD expansion card.
What are PCIe x8 Slots Used for?
PCIe x8 Slots work well with advanced hardware devices like NVMe M.2 expansion cards and high-definition capture cards, and so on. Coming with 8 PCIe lanes, the PCIe x8 slots are double the bandwidth of a PCIe x4 slot.
What are PCIe x16 Slots Used for?
The PCIe x16 slots are used for high-end hardware expansion cards like graphics cards. Graphics cards have to transfer lots of data every second to the motherboard for video and graphics rendering. Therefore, they require a high-bandwidth slot like PCIe x16 slots.
Now, the point you should note is that the PCIe slots are also categorized in form of generations other than sizes. Here are the main PCIe generations:
So, What Are PCIe Slot Generations?
Below are the MAIN PCIe generations:
- PCIe 1.0
- PCIe 2.0
- PCIe 3.0
- PCIe 4.0
- PCIe 5.0
- PCIe 6.0
Wondering about the transfer rates and performance of these PCIe slot generations? Well, they double with every next generation (we’ve created a detailed table below).
Commonly Used PCIe Slot Generations – PCIe 1.0 Through 4.0
Out of the PCIe generations listed above, the four are the common ones:
- PCIe 1.0
- PCIe 2.0
- PCIe 3.0
- PCIe 4.0
If you’re wondering what sort of performance you’d get on using a PCIe expansion card on any of these generations, it’ll be equivalent to the lowest generation either way.
For instance, if you connect a 2.0 generation expansion card on a 4.0 generation slot, you’ll only get the performance of the 2.0 generation.
Out of these 4, PCIe 4.0 is a kinda modern generation and a big upgrade that came out in 2017. It offered bandwidth of 64 Gbps and.
Modern PCIe Generations – PCIe 5.0 and PCIe 6.0
PCIe 5.0 and PCIe 6.0 are the modern standards for PCIe slots.
PCIe 5.0 generation was released in 2019 and carried a remarkable 128 GBps bandwidth. It offered compatibility with the previous PCIe generations and brought forth extra features like:
- Improved electrical system
- Compatibility with previous PCIe versions
However, the point to note is, only the standard has come out, not the devices. They’re expected to release in 2022.
Anyway, it is predicted that PCIe 5.0 will only be available for data centers and enterprise-level computers – PCIe will remain the standard for personal systems.
When it comes to the PCIe 6.0 generation, it doubles the throughput of the previous generation and is also backward compatible. However, companies predict that PCIe 6.0 devices won’t release anytime before the end of 2022.
Comparison of PCIe Slot Generations
Below is a little comparison of PCIe slot generations that covers their bandwidth, frequency, and gigatransfer rates.
| Generation | Gigatransfer | Frequency | Bandwidth |
| PCIe 1.0 | 2.5 GT/s | 2.5 GHz | 8 GB/s |
| PCIe 2.0 | 5 GT/s | 5 GHz | 16 GB/s |
| PCIe 3.0 | 8 GT/s | 8 GHz | 32 GB/s |
| PCIe 4.0 | 16 GT/s | 16 GHz | 64 GB/s |
| PCIe 5.0 | 32 GT/s | 32 GHz | 128 GB/s |
| PCIe 6.0 | 64 GT/s | 32 GHz | 256 GB/s |
With that said, it’s important to keep your motherboard dust-free to ensure all its components work fine. Read our guide on how to clean a motherboard to learn more about that
Does it Matter Which PCIe x16 Slot I Use?
Yes, the PCIe x16 slot you use does matter. This is because PCIe x16 is the fastest size for PCIe slots and most motherboards have it on the first. The next slots generally are of smaller size. So, it’s recommended to use PCIe x16 slot for maximum bandwidth and performance.
What to Put in PCIe Slots?
Below are the major devices that can be plugged into the PCIe expansion slots:
1. Video Capture Cards – to convert an analog video signal
2. M.2 NVMe Expansion Cards – to add additional storage
3. TV Tuner Cards – to receive television signals
4. Wireless + Bluetooth Network Cards – for wireless internet
5. Graphics Cards – for better graphical power
6. SATA Expansion and RAID Controller Cards – to add more optical drives
7. Sound Cards – to produce sound on the computer
8. Ethernet Network Cards – for wired Ethernet connections
9. Port Expansion Cards – for additional ports on the computer
10. Riser / Splitters – to extend a slot for an I/O card
Are PCIe Slots Compatible With Slot Cross?
The slot cross-compatibility refers to installing a device with a lower lane coin into a slot with a higher lane count.
Thankfully, the PCIe system is designed in a way to make this possible.
For instance, if you have an expansion card (like a Wifi card) that is PCIe x4 (4 lanes) and the only slot available is PCIe x8, then it might be possible to install the card into this slot. In fact, the expansion card will work properly.
However, you’ll get the lowest bandwidth of either slot or the expansion card. Let me explain:
Using an expansion card with a lower lane count compared to the lane count of the slot you’re putting it into will result in the bandwidth of the slowest hardware part.
So, if you put a PCI x1 card into a PCI x4 slot, the performance will be equivalent to PCI x1 at the end of the day.
Are PCIe Slots Backward Compatible?
Other than the cross-slot compatibility, backward compatibility is another major highlight of the PCIe standard.
Meaning you can install an expansion card with a higher lane count into a slot with a lower lane count, as long as the card fits (depending on the size).
For instance, if a card with PCIe lane x8 is put into a PCIe x4 slot, it might work just fine.
Another point to note is, these compatibility rules also apply to PCIe versions. So, you can put a PCIe 2.0 device into PCIe 4.0. But again, the performance is equivalent to the lowest connection.
Sorry to disturb you but determining how many SATA cables you want can be tempting. Read our guide on how many SATA cables do I need to find out more about that.
How to Identify PCIe Slots
The best way to identify PCIe slots is by determining the size of PCIe slots on your motherboard. Simply open your PC case and know that the first PCIe slot is a PCIe x16 in most cases.
After that, you might find a PCIe 8x slot and then a PCIe 4x. However, the order can be slightly (or significantly) different depending upon the motherboard.
Furthermore, you can also look into the image below for convenience:
Real-Time Example for PCIe Slot Configuration
The above image is a live example of how to determine PCIe slot configuration.
As you can see, the first PCIe slot is the x16 size while the next one is x8. Now, these do come in the same sizes but have different lane counts.
Next to the PCIe, x8 configuration is the PCIe x4 configuration which follows PCIe x1.
Most of the ATX standard motherboards come with such a configuration order. But the case is not always the same. Some motherboards might also have a different order.
For instance, a high-end motherboard could have a PCIe x32 configuration at the start. Similarly, an old-school motherboard could have the PCIe 8x configuration. It depends upon many factors of the motherboard like form factor, budget, and so on.
Anyway, below are the images of a few motherboards with different configuration orders:
Motherboard 1:
Motherboard 2:
Video for Understanding PCIe Standard
With all of that said, below is a helpful video you can go through quickly, for understanding what PCIe Express is:
Other Motherboard-Related Guides
Does DDR5 RAM Work on the DDR4 Motherboard? — Find out whether DDR5 RAM is going to be backwards compatible or not.
How Can I Troubleshoot a Motherboard? — Discover the 10 most effective ways to troubleshoot am motherboard with minimal effort.
What are Standoffs on Motherboards? — Learn what motherboard standoffs are why they’re so important, and where you can get them.
Final Words
That’s pretty much it. I hope this guide helped you find out what are PCIe slots and their uses. To recap, PCIe slots work as expansion slots that let you install further hardware on the motherboard. It could be a graphics card or a port expansion card.
With that out of the way, do share the article if you liked it.
What part did you find the most interesting? Let me know in the comments.

![Does Motherboard Matter for Gaming? [Complete 2024 Guide]](https://motherboardtimes.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/does-motherboard-matter-for-gaming-768x432.png)

![Do Motherboards Come With Wi-Fi? [Detailed Guide]](https://motherboardtimes.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/do-motherboards-come-with-wifi-1-768x512.jpg)
![How to Know if a Motherboard Will Fit in My Case [Simplified]](https://motherboardtimes.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/how-to-tell-if-a-motherboard-will-fit-in-my-pc-case-768x432.jpg)
![Can Motherboard Bottleneck GPU in 2024 [ + Infographic]](https://motherboardtimes.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/can-motherboard-bottleneck-gpu-768x432.png)